Next-generation data storage
The era of exponential data growth needs new storage solutions. This is how imec’s researchers will enable future applications to pack more information on a smaller surface.
The market for non-volatile memories is expected to keep on growing considerably year after year. This is driven by exponential developments in data centers, the IoT, and mobile applications. As with logic scaling, simple dimensional scaling can no longer provide the necessary growth per unit for cost and efficiency.
Therefore, new processes, memory devices, materials, and even storage concepts will be needed. Imec is working on all these levels to provide the industry with promising, manufacturable solutions.
NAND storage technology, as used in flash memory, is expected to keep scaling incrementally. In the first years, this will be enabled by continued 3D stacking. Later on, more disruptive changes will be called for.
3D scaling of NAND storage
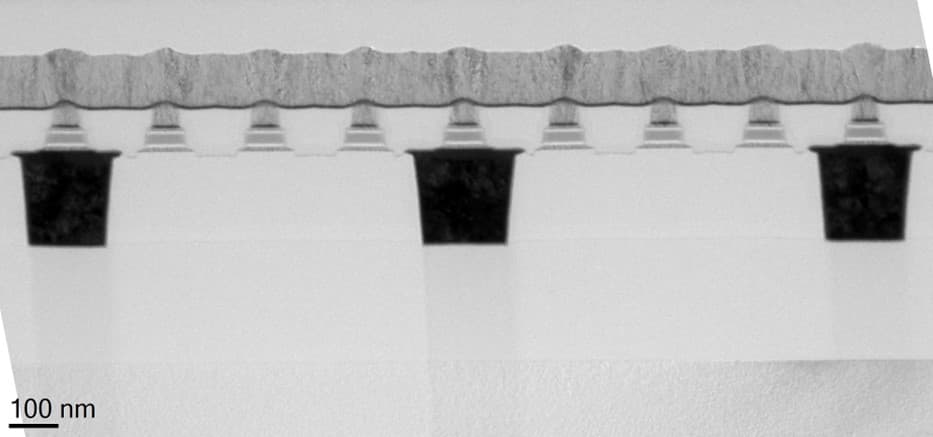
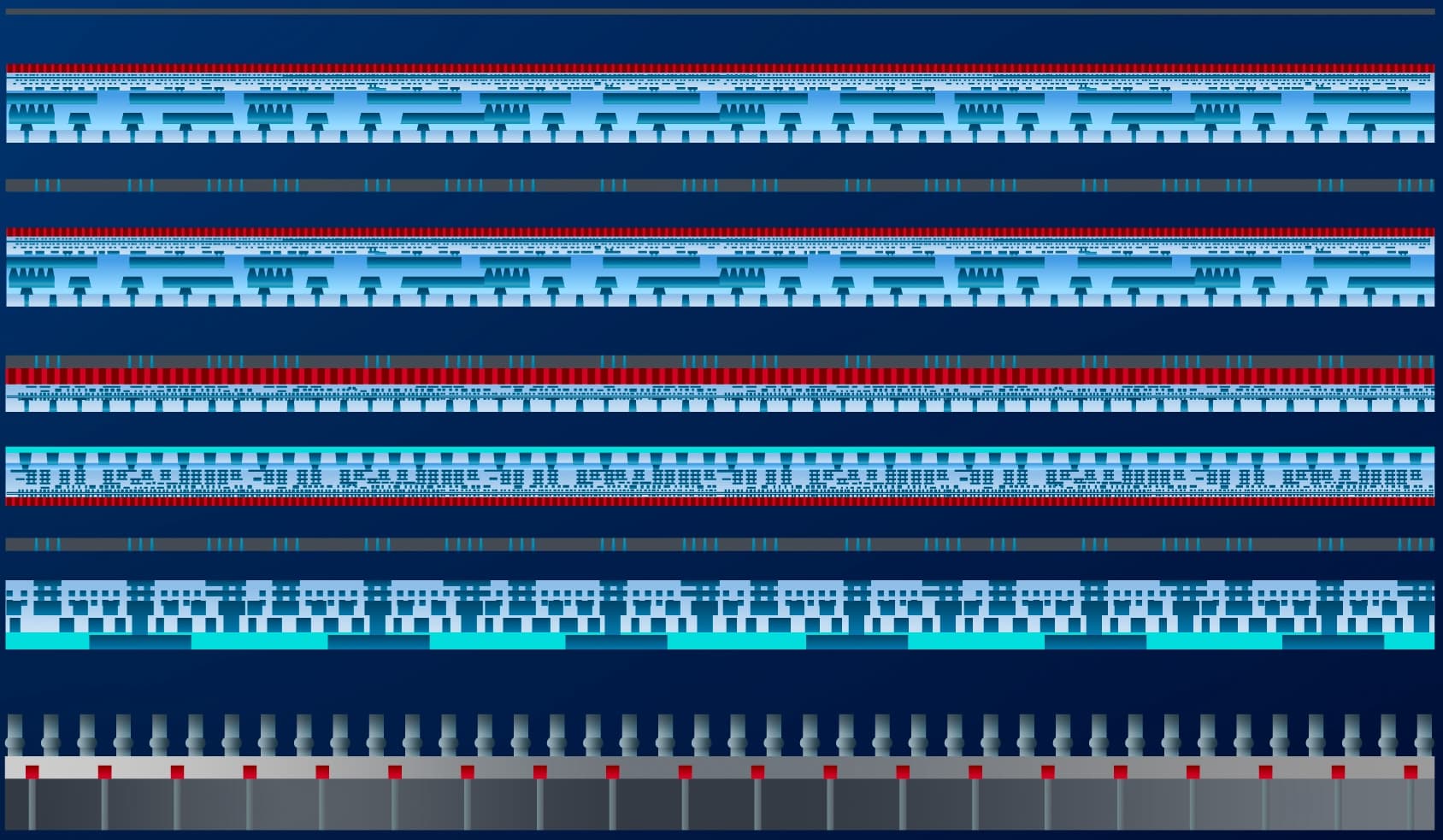
At the start of the 2020’s, most advanced NAND products featured 128 layers of storage capacity. 3D scaling will continue by adding additional layers, potentially enabled by wafer-to-wafer bonding.
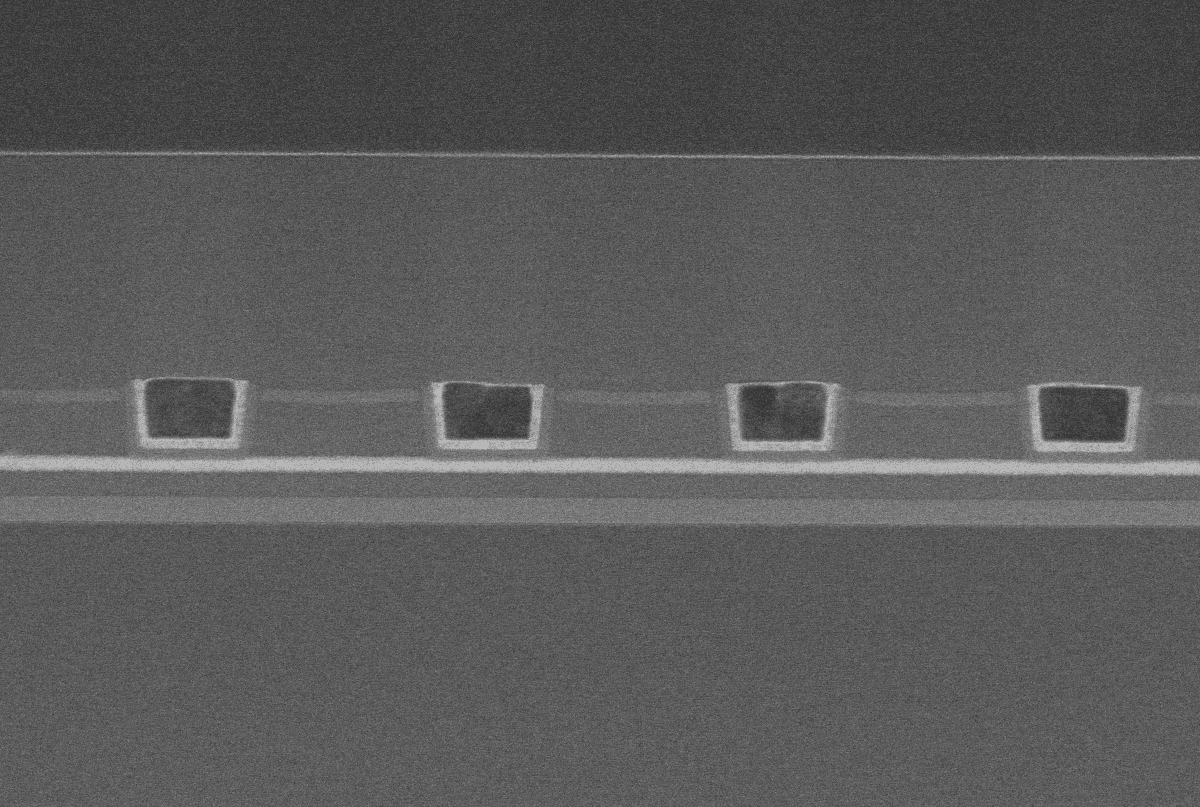
Schematic representation of a 3D-NAND Flash structure.
Imec contributes to this roadmap by developing new low-resistance word-line metals, researching alternatives for the memory dielectric stacks, improving the channel current, and identifying ways to control the stress that evolves due to the growing number of stacked layers.
Our scientists also focus on replacing the planar logic transistors in the NAND periphery with more advanced FinFET devices.
Novel data storage concepts
For the longer term, we explore 3D ferroelectric FETs (FeFETs) with novel materials as an alternative for flash memory in high-end storage applications. These vertical FeFETs have several advantages, including:
- simplified processing
- higher speed
- lower power usage
Moreover, compared to 3D-NAND, vertical FeFETs can potentially be programmed at much lower voltages, which promises improved reliability and scalability.
Finally, imec is also looking beyond 3D NAND, for the era where storage will reach terabits per square millimeter. We are evaluating the suitability of a range of new memory concepts, including liquid-based and DNA-inspired memories.